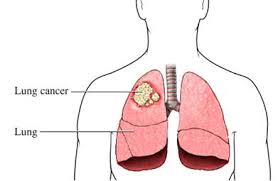
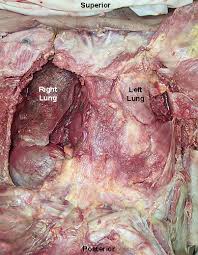
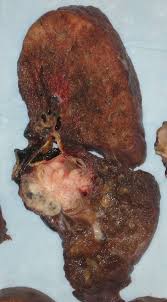
Lung Cancer Biography
(Source google.com)
The most common cause of lung cancer is long-term exposure
to tobacco smoke, which causes 80–90% of lung cancers. Nonsmokers account for
10–15% of lung cancer cases, and these
cases are often attributed to a combination of genetic factors, and exposure to;
radon gas, asbestos, and air pollution including second-hand smoke. Lung cancer
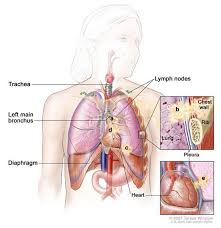
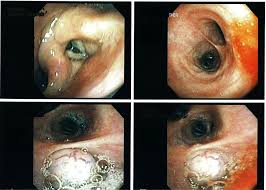
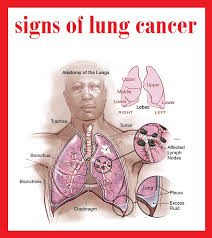
may be seen on chest radiographs and computed tomography(CT) scans. The
diagnosis is confirmed by biopsy which is usually performed bybronchoscopy or
CT-guidance. Treatment and long-term outcomes depend on the type of cancer, the
stage (degree of spread), and the person's overall health, measured
byperformance status. Common treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, and
radiotherapy. NSCLC is sometimes treated with surgery, whereas SCLC usually
responds better to chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Overall, 15% of people in the
United States
diagnosed with lung cancersurvive five years after the diagnosis. Outcomes are
worse in the developing world. Worldwide, lung cancer is the most common cause
of cancer-related death in men and women, and is responsible for 1.38 million
deaths annually, as of 2008.
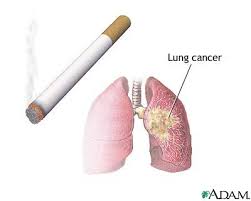
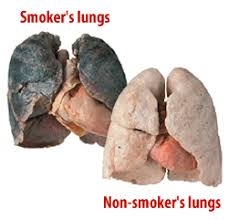
Smoking, particularly of cigarettes, is by far the main
contributor to lung cancer. Cigarette smoke contains over 60 known carcinogens,
including radioisotopes from the radon decay sequence, nitrosamine, and
benzopyrene. Additionally, nicotine appears to depress the immune response to
cancerous growths in exposed tissue. Across the developed world, 90% of
lung cancer deaths in men during the year 2000 were attributed to smoking (70%
for women). Smoking accounts for 80–90% of lung cancer cases. Passive smoking—the inhalation of smoke from another's
smoking—is a cause of lung cancer in nonsmokers. A passive smoker can be
classified as someone living or working with a smoker. Studies from the US , Europe, the UK ,
and Australia
have consistently shown a significantly increased risk among those exposed to
passive smoke. Those who live with someone who smokes have a 20–30% increase in
risk while those who work in an environment with second hand smoke have a
16–19% increase in risk. Investigations of sidestream smoke suggest it is more
dangerous than direct smoke. Passive smoking causes about 3,400 deaths from
lung cancer each year in the USA .
Radon is a colorless and odorless Europe, the UK , and Australia have consistently shown a significantly increased risk among those exposed to passive smoke. Those who live with someone who smokes have a 20–30% increase in risk while those who work in an environment with second hand smoke have a 16–19% increase in risk. Investigations of sidestream smoke suggest it is more dangerous than direct smoke. Passive smoking causes about 3,400 deaths from lung cancer each year in the USA . Radon is a colorless and odorless gas generated by the breakdown of radioactive radium, which in turn is the decay product of uranium, found in the Earth's crust. The radiation decay products ionize genetic material, causing mutations that sometimes turn cancerous. Radon is the second-most common cause of lung cancer in the USA , after smoking. The risk increases 8–16% for every 100 Bq/m³ increase in the radon concentration. Radon gas levels vary by locality and the composition of the underlying soil and rocks. For example, in areas such as Cornwall in the UK (which has granite as substrata), gas generated by the
breakdown of radioactive radium, which in turn is the decay product of uranium,
found in the Earth's crust. The radiation decay products ionize genetic
material, causing mutations that sometimes turn cancerous. Radon is the
second-most common cause of lung cancer in the USA , after smoking. The risk
increases 8–16% for every 100 Bq/m³ increase in the radon concentration. Radon
gas levels vary by locality and the composition of the underlying soil and rocks.
For example, in areas such as Cornwall in the UK (which has
granite as substrata), radon gas is a major problem, and buildings have to be
force-ventilated with fans to lower radon gas concentrations. The United States
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimates one in 15 homes in the US has radon
levels above the recommended guideline of 4 picocuries per liter (pCi/l) (148
Bq/m³).





No comments:
Post a Comment